Keylogger Protection
- Home
- Keylogger
What is a Keylogger?
A keylogger, otherwise known as a keystroke logger, is a malicious program or device made to log and register nearly every keystroke you type, frequently obtaining private information such as passwords, usernames, credit card numbers, or private messages. Keyloggers can be software or hardware based.
Unlike other malware that might corrupt or encrypt data, keyloggers are stealthy tools focusing on silently collecting what you type. They send this data back to attackers, who are using this information for credential theft, identity fraud, or corporate espionage.
Modern keyloggers are capable of hooking deep within system processes and intercepting keystroke strokes typed in by various input methods, such as on-screen keyboards or copy-paste buffers, making them ever more difficult to detect.
Different Types of Keyloggers:
- Software Keyloggers: Hidden in the operating system, software keyloggers log keys pressed on a computer through the use of kernel drivers or low-level Application Program Interfaces (APIs).
- Hardware Keyloggers: Hardware keyloggers are physical devices that usually connect to the computer at the base of the keystroke device.
- Kernel-Based Keyloggers: Kernel-based loggers hook directly to the kernel of the operating system, thus making it exceedingly challenging for antimalware software to detect them.
- Form Grabbing Keyloggers: These target form inputs in browsers, recording what you type into a login form or search bar.
- Remote Access Keyloggers: Bundled with trojans; the attacker can retrieve logs from infected systems.
Popular Keylogger Malware:
- Agent Tesla: A RAT (Remote Access Trojan) infamous for its highly developed keylogging capabilities.
- HawkEye: Hawkeye specializes in stealing credentials from browsers and email clients, logging every keystroke.
- KeyBase: Intercepts real-time form data, focusing on financial and e-commerce sites.
- Olympic Vision: A hardware-based installation that implants itself using keyboard cable or USB ports to sniff keystrokes offline.
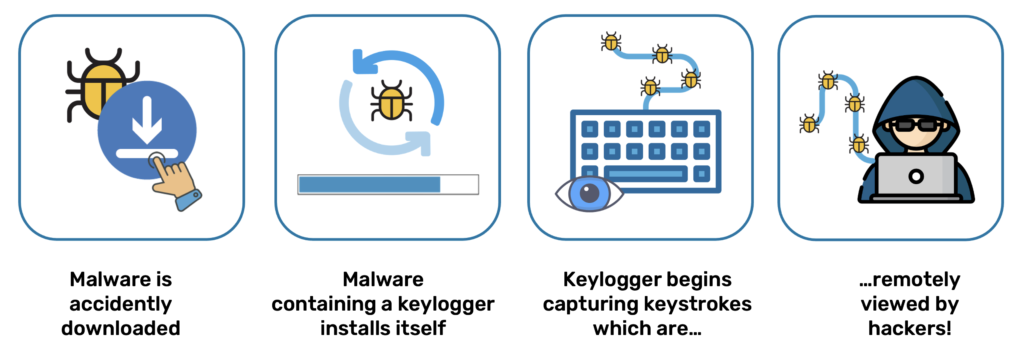
How Keyloggers Infect You:
- Phishing Emails: They contain malicious attachments or links that perform their installations on your device once perused.
- Drive-by Downloads: Visiting a website that has already been compromised to exploit the loopholes in browsers.
- Trojan Bundles: Keyloggers are bundled with a trojan in a course because they control remotely infected systems.
- Physical Installation: Attackers have the option of plugging hardware keyloggers in between a keyboard and the computer or embedding them into the internal wiring of the laptop.

How Keyloggers Operate:
- System Hooks: Operating at the OS level, these intercept keyboard events that record every keystroke.
- Stealth Storage: It stores logs in a file, registry key, or memory buffer that is not visible or easily reachable to attackers.
- Form & Clipboard Capture: Some types are aimed at password fields or copy-pasted credentials.
- Exfiltration: Logs are periodically sent out through e-mail, FTP, or direct server connection, sometimes encrypted.
Consequences:
- Identity theft and unauthorized financial transactions
- Compromised corporate networks via stolen admin credentials
- Personal data breaches, leaking private messages or accounts
- Long-term spying without evident system damage
How OmniDefender Protects You:
- Behavioral Analysis: Detects keyboard-hooking or process-injecting activity that is unusual or abnormal and calls out the suspected keylogger.
- Keystroke Encryption: Optionally encrypts keystokes at the driver level to protect against logging in clear text.
- Anti-Hook Detection: Scans for hidden kernel hooks or uses user-mode API hooking techniques.
- Real-Time Alerts: Returns real-time alerts whenever OmniDefender finds a suspected logging activity.
Advanced Keylogger Defense System
Live Keystroke Monitoring
Watches for suspicious programs trying to hook keyboard events, instantly halting unauthorized logging.
Secure Backup & Restore
Safeguards critical system files and drivers, letting you revert to a clean state if a keylogger hijacks your OS.
AI-Based Suspicion Engine
Leverages heuristic patterns to identify advanced or newly emerging keylogger variants lacking known signatures.
Driver Verification
Blocks installation of unsigned or suspicious kernel drivers often used by stealth keyloggers for deep-level hooking.
How to Protect Yourself from Keyloggers
Essential Security Practices:
- Strong Password Hygiene: Use good, complex passwords and change them often to minimize the damage caused by keyloggers stealing information.
- Frequent Updates: Update your OS, AV software, and browsers to fix the exposed vulnerabilities that install keyloggers.
- Email Caution: Do not open potentially dangerous attachments; they might quietly install hidden software keyloggers.
- Inspect Hardware: Routinely check your keyboard plug to see if some strange device is inserted between the cable and port.
Advanced Protection Measures:
- Keystroke Encryption Tools: Understand the difference between encryption software that encrypts your keystrokes at the driver level.
- Application Whitelisting: Only allow known, trusted, executables, and avoid using unsigned/unknown applications.
- USB Security: Retroactively disable ports when possible to prevent hardware keylogger installation.
- 2FA Everywhere: Having a two-factor authentication security measure on top of passwords makes sure that even if attackers log your password, they will have trouble bypassing it.
Emergency Preparedness:
- Incident Response Plan: Put in place policies to indicate how suspected keylogger infections will be isolated and communicated to key stakeholders.
- Offline Backups: Back up data that has already been unplugged from an OS to minimize the potential for infiltration.
- Hotspot Monitoring: Scan for any abnormal traffic from your Wi-Fi connection, indicating some logs could be directed to an external server.
- Forensic Tools: Use specific scanning utilities on your system for deeper offline checks of OS hooks and driver layers.
Daily Best Practices:
- Scheduled AV Scans: Run OmniDefender’s advanced keylogger detection scans daily or weekly.
- Use On-Screen Keyboards Sparingly: Some keyloggers also capture screen clicks; treat them as partial security measures.
- Be Vigilant with Public PCs: When traveling, assume public computers may be hardware- or software-logged.
- Educate Staff/Family: Regular cybersecurity training helps everyone spot potential keylogger threats.