Fileless Malware Protection
- Home
- Fileless Malware
What is Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is an advanced type of offensive used by cyber attackers that does not rely on creating a malicious file on the drive. Instead, it actually resides in the system memory and legitimate processes in the operating system, like PowerShell and WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation). Because of that, it becomes very difficult to detect it through classic antivirus.
Fileless threats do not generate new files or write to the registry, unlike their conventional counterparts. Instead, they abuse trusted system components or processes to launch attacks—for instance, to steal data or execute lateral movement across the network.
Many of the modern fileless malware use clever evasion techniques, often disabling the security services in such a way that they erase their own presence from memory on reboot, only to reestablish a presence when requested.

Different Types of Fileless Malware:
- PowerShell Exploits: Abuses legitimate PowerShell scripts to download or execute malicious code purely in memory.
- WMI-Based Attacks: Uses Windows Management Instrumentation to run harmful commands without writing new files.
- Code Injection: Injects malicious code into existing, trusted processes (e.g., explorer.exe) to mask activity.
- Memory-Resident Malware: Survives only in RAM, vanishing when the system reboots—unless triggered again later.
- Browser Exploits: Targets browser memory space (e.g., Chrome, Firefox) to steal data or hijack sessions.
Popular Fileless Malware Examples:
- DoublePulsar: A backdoor exploit leveraged by the EternalBlue vulnerability to run shellcode entirely in memory.
- FIN7 Attacks: Known for using PowerShell scripts and fileless tactics to target financial institutions.
- Operation Cobalt Kitty: A sophisticated campaign that used fileless WMI-based intrusion to breach corporate networks.
- SamSam: Combined fileless techniques with ransomware execution, bypassing many standard antivirus solutions.
How Fileless Malware Infects You:
- Phishing Emails: Malicious macros or scripts activate memory-resident code upon opening an infected document.
- Exploiting OS Tools: Uses pre-installed utilities (PowerShell, WMI, etc.) to download or run payloads stealthily.
- Drive-by Exploits: Hidden scripts on compromised sites that run in the background once you visit.
- Credential Abuse: Gains legitimate admin privileges to run fileless scripts or tasks system-wide.
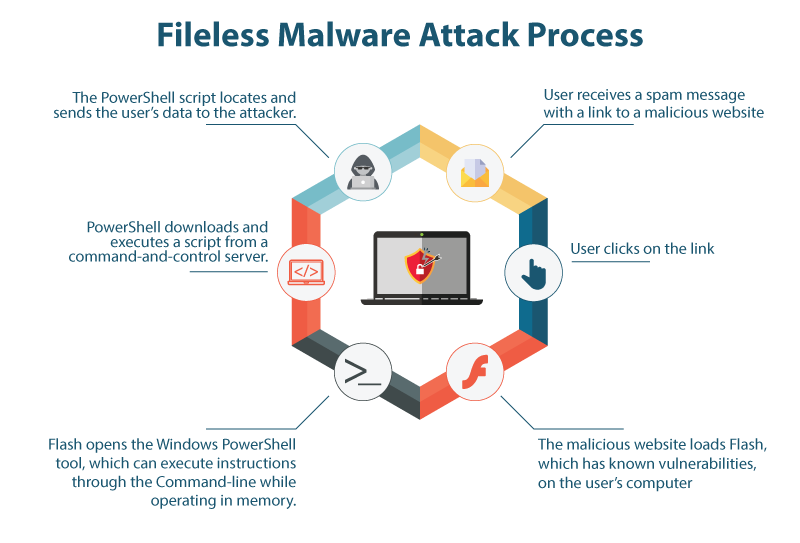
How Fileless Malware Operates:
- Abuse of System Tools: Uses legitimate processes, like powershell.exe or svchost.exe, to mingle with normal operations.
- Memory-Only Persistence: Leaves very minimal or no trace on the disk and evades file-based detection.
- Lateral Movement: Will be moving across networks through the exploitation of admin credentials or misconfigurations, and installing more code which stays only in memory.
- Stealth & Cleanup: Wipes logs when it finishes tasks, or kills processes upon task completion without creating any suspicious artifacts.
Consequences:
- Undetected infiltration leading to data exfiltration or sabotage
- Use of legitimate tools making detection and forensic analysis difficult
- Potential spread to multiple hosts in large corporate networks
- Severe financial and reputational harm once an attack surfaces
How OmniDefender Protects You:
- Behavior Monitoring: Keeps an eye out for unusual PowerShell or WMI calls and alerts you of memory-resident threats.
- Memory Scanning: It periodically scans volatile memory for known malicious signatures and suspicious behaviors.
- Privilege Management: Make recommendations about the best practices for restricting admin tools to authorized personnel only.
- Instant Containment: Quarantines suspected processes quickly, preventing further fileless code execution.
Advanced Fileless Malware Defense System
Live Process Inspection
Continuously inspects active processes and services for signs of malicious injection or unauthorized script execution.
Data Backup & Recovery
Ensures regular backups are created offline, so memory-resident threats can’t tamper with your restore points.
AI-Enhanced Heuristics
Identifies suspicious memory or network behaviors, detecting new and evolving fileless methods that lack classic malware signatures.
System Hardening
Locks down or restricts critical tools like PowerShell and WMI, reducing potential abuse vectors for fileless attacks.
How to Protect Yourself from Fileless Malware
Essential Security Practices:
- Patch Management: Never skip regular operation system and application updates. This helps you in plugging new zero-day vulnerabilities that are in the OS and apps.
- Harden System Tools: Try to cut the risk of infection by not letting non-admin users to use the PowerShell or WMI or at least, they are allowed with limited use of these tols.
- Email Caution: Browse through attachments to be sure they are legitimate. Also, consider running macros.
- Robust Credentials: Try to use stronger passwords in combination with Multi-Factor Authentication to mitigate any unauthorized access attempts.
Advanced Protection Measures:
- Application Control: Use whitelisting which is a powerful tool that authenticates that the files are not malware and therefore can run or system tools can be called.
- Network Segmentation: Keep your LAN divided to prevent the malware from spreading in the whole network.
- Threat Intelligence: Remain knowledgeable on the latest IoCs and attack patterns for fileless campaigns in order to follow evolving threats.
- Regular System Audits: Focus attention on every abnormal event logs and memory usage that indicate genuine threats.
Emergency Preparedness:
- Incident Response Plan: You can solve the problem faster by including the action plan that is specific for this kind of incident (memory threat).
- Offline Backups: Protect your backups that are let fed with the main company data. If devices from the network segment are disconnected, these backups will also be safer, and are there no chance of memory-based threats affecting them.
- Emergency Contacts: Save the names and numbers of the cybersecurity experts and relevant authorities and keep them within reach.
- Forensic Tools: We recommend you to have memory forensics software to capture live system snapshots if an infection is suspected.
Daily Best Practices:
- Scheduled Deep Scans: By using OmniDefender's next-level scanning make sure to catch any computer processes using the system abnormally or any hidden code injection does.
- Minimize Admin Rights: Give elevated rights with caution so that the risk is minimal if a person becomes a victim of an account that has been compromised.
- Monitor System Behavior: Examine traffic that may reflect fileless activities otherwise the resource spikes and network requests might be found to imply.
- Regular Training: People should familiarize themselves with all the techniques that are used by hackers to get personal information. Such as elementary concepts like safe surfing and phishing, as well as fileless threats, must also be included in the training.