Intrusion Detection (Network Based)
- Home
- Intrusion Detection
What is Network-Based Intrusion Detection?
A Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) monitors the inbound and outbound traffic on your network in real time, looking for unauthorized, malicious, or abnormal patterns of behavior. It analyzes network packets, compares them to known threat signatures, and uses behavior analysis to detect zero-day exploits or policy violations.
They are distinctly different from host-based intrusion detection in that network-based systems analyze traffic at certain strategic points within the infrastructure—such as firewalls, routers, or dedicated sensors—to detect threats affecting all devices connected to the network.
Modern NIDS solutions often use a blend of machine learning and behavioral analytics to catch mild anomalies such as spikes in traffic and unauthorized data transfers, allowing your security team the required time to respond before extensive damage is dealt to the organization.
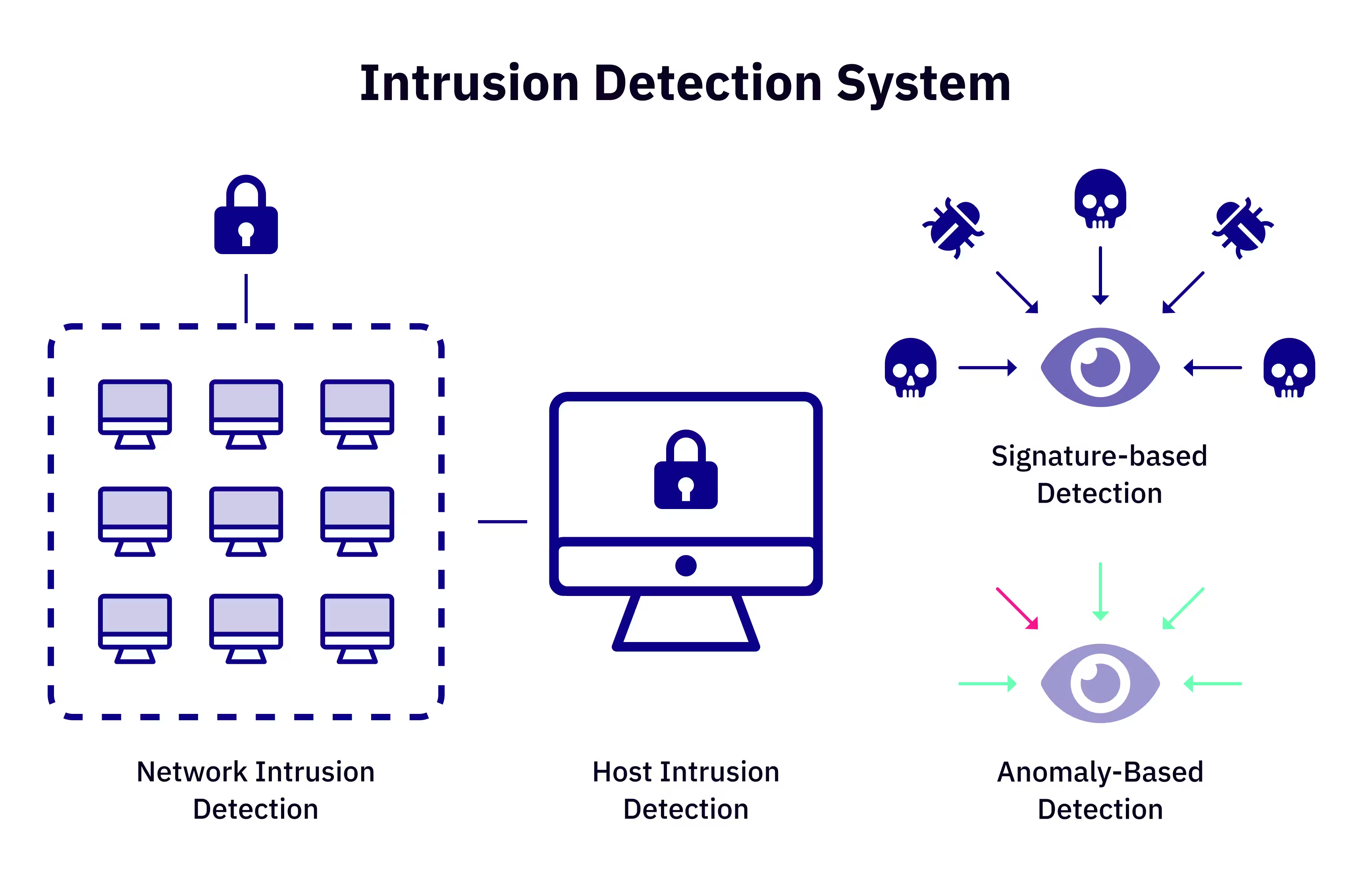
Different Types of NIDS:
- Signature-Based NIDS: Searches through a database of known attack patterns (signatures) to identify malicious traffic.
- Anomaly-Based NIDS: It establishes a baseline for normal behavior on the network and flags any deviations from that baseline that may indicate an attack.
- Policy-Based NIDS: It triggers surveillance (alert) when network traffic violates defined security policies or organizational compliance rules.
- Hybrid NIDS: It employs the combination of all three methods of detecting the signature (based on AV), anomaly or behavior (based on statistics), and policy-based (based on rules) to ensure accuracy and minimize false positives.
Popular NIDS Technologies:
- Snort: One of the most widely used open-source NIDS systems; with a superb rule-set and a strong user community.
- Suricata: NIDS/NIPS which uses multi-threading, has high performance features, and advanced features for threat detection.
- Zeek (formerly Bro): Involves some high-level analysis of traffic and provides powerful scripting for custom anomaly detection.
- OSSEC (with NIDS modules): Protect mainly host-based, but sometimes does provide the opportunity to take advantage of network logs for a larger picture.
How Network IDS Detects Threats:
- Packet Analysis: The headers of the packets and the payloads of the packets are examined for known exploit signatures.
- Flow-Based Monitoring: Checks connections and masks dubious volumes, time, or protocol anomalies, looking out for rejected flows.
- Behavioral Insights: Once the establishment of a traffic baseline has been done, it raises alarms if unusual flow patterns begin to emerge-e.g., large exfiltration or port scans.
- Real-Time Alerts: We notify security groups through dashboards, SIEM integration, or direct syslog feeds.
Consequences:
- Elimination of advanced persistent threats (APTs) long before they get a chance to compromise crucial data.
- Reduction of time to respond to incidents, hence contain the damage and spread of intrusions.
- Visibility into the patterns of network usage, pointing to hidden vulnerabilities or configuration mistakes.
- Other advantages relate to regulatory compliance and the ability to showcase proper monitoring and breach-prevention
How OmniDefender Protects You:
- Deep Packet Inspection: Perform advanced packet parsing functions, to detect hidden payloads or obfuscated malicious content.
- Encrypted Traffic Analysis: Make use of metadata and behavioral patterns in the SSL/TLS flows to identify potential threats without having to decrypt content.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Integration with global threat databases to effectively block new discovery-based attack signatures.
- Real-Time Event Correlation: Collecting alerts from multiple network segments to correlate to unveil coordinated attacks.
Advanced NIDS Defense System
Intelligent Traffic Inspection
Continuously monitors all network segments, applying signature and anomaly detection to identify threats in real time.
Incident Logging & Recovery
Retains detailed packet captures and logs for forensics, assisting swift incident response and remediation.
Machine Learning Insights
Detects zero-day exploits by learning normal network behaviors, raising alerts on hidden anomalies or malicious patterns.
Dynamic Threat Updates
Automatically syncs new signatures and rulesets from OmniDefender’s global threat intelligence to protect against emerging attacks.
How to Protect Yourself from Network Intrusions
Essential Security Practices:
- Network Segmentation: Divide the local area network clusters into subnetworks and restrict damage traffic within the cluster.
- Strong Access Controls: Ensure best practices with firewalls, employment of VLANs, and limit the privilege across network devices.
- Stay Patched & Updated: Always upgrade firmware on routers, switches, and NIDS sensors to counter the information security threats.
- Visibility & Logging: Enable netflow logging and event auditing for insights into network activities.
Advanced Protection Measures:
- Inline NIPS: Deploy Intrusion Prevention modules that will not only detect but also take automatic action to block malicious traffic.
- Encrypted Traffic Analysis: Analysis: Monitor SSL/TLS connections with known-bad domains or suspicious certificate behaviors.
- Deception Technologies: Deployed honeypots, honeynets, etc., used to lure attackers and collect intelligence without putting real assets at risk.
- SIEM Integration: Correlate events with logs from other systems for a more expansive view of threat detection.
Emergency Preparedness:
- Incident Response Plan: Decide how segment isolation of network clusters will be done, blocking of malicious source IPs, and intention to notify other relevant teams.
- Offline Backups: Guarantee disconnecting critical configs and data backups from the main network to restore soon after attacks.
- Emergency Contacts: Maintain ready contact for ISP, cybersecurity experts, and authorities for immediate escalation during a breach incident.
- Forensic Capabilities: Employ packet capture and offline analysis tools to dissect intrusions and boost defenses.
Daily Best Practices:
- Scheduled Scans: Regularly run the OmniDefender's Smart scan to capture on-taking threats or misconfigurations.
- Monitor Network Baselines: Any unusual spike or drop on traffic means there rarely means some infiltration or data exfiltration is going on.
- Regular Staff Education: Staying abreast of phishing tactics and insider threat awareness to alleviate risky behavior among employees.
- Frequent Firmware Updates: Keep updating your network appliances with their firmware to most recent in order to close the exploits.